|
Practical Renewable Energy Solutions |
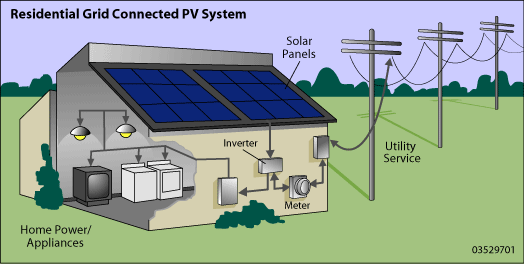
How Small Solar Electric Systems Work
Solar electric systems, also known as photovoltaic (PV) systems, convert sunlight into electricity.
Solar cells, the basic building blocks of a PV system, consist of semiconductor materials. When sunlight is absorbed by these materials, the solar energy knocks electrons loose from their atoms. This phenomenon is called the "photoelectric effect." These free electrons then travel into a circuit built into the solar cell to form electrical current.. Only sunlight of certain wavelengths will work efficiently to create electricity. PV systems can still produce electricity on cloudy days, but not as much as on a sunny day.
The basic PV or solar cell typically produces only a small amount of power. To produce more power, solar cells (about 40) can be interconnected to form panels or modules. PV modules range in output from 10 to 300 watts. If more power is needed, several modules can be installed on a building or at ground-level in a rack to form a PV array. About 10 to 20 PV arrays can provide enough power for a household.
PV arrays can be mounted at a fixed angle facing south, or they can be mounted on a tracking device that follows the sun, allowing them to capture the most sunlight over the course of a day.
Because of their modularity, PV systems can be
designed to meet any electrical requirement, no matter how large or how small.
You also can connect them to an electric distribution system (grid-connected),
or they can stand alone (off-grid).